Content

Under shareholder’s equity, accounts are arranged in decreasing order of priority. If a company or organization is privately held by a single owner, then shareholders’ equity will generally be pretty straightforward. If it’s publicly held, this calculation may become more complicated depending https://www.bookstime.com/articles/construction-in-progress-accounting on the various types of stock issued. The expanded accounting equation can be rearranged in many ways to suit its use better. With that being said, no matter how the formula is laid out, it must always be balanced. Additionally, it doesn’t completely prevent accounting errors from being made.

External auditors, on the other hand, might use a balance sheet to ensure a company is complying with any reporting laws it’s subject to. Here’s everything you need to know about understanding a balance sheet, including what it is, the information it contains, why it’s so important, and the underlying mechanics of how it works. It can be sold at a later date to raise cash or reserved to repel a hostile takeover. Some liabilities are considered off the balance sheet, meaning they do not appear on the balance sheet. Our easy online application is free, and no special documentation is required. All applicants must be at least 18 years of age, proficient in English, and committed to learning and engaging with fellow participants throughout the program.
Introduction of Balance Sheet Equation
As you can see, shareholder’s equity is the remainder after liabilities have been subtracted from assets. This is because creditors – parties that lend money such as banks – have the first claim to a company’s assets. For example, an increase in an asset account can be matched by an equal increase to a related liability or shareholder’s equity account such that the accounting equation stays in balance. Alternatively, an increase in an asset account can be matched by an equal decrease in another asset account.
- An analyst can generally use the balance sheet to calculate a lot of financial ratios that help determine how well a company is performing, how liquid or solvent a company is, and how efficient it is.
- Last, a balance sheet is subject to several areas of professional judgement that may materially impact the report.
- Liabilities are what a company owes to others—creditors, suppliers, tax authorities, employees, etc.
- Or in other words, it includes all things of value that are used to perform activities such as production and sales.
- Because there are two or more accounts affected by every transaction carried out by a company, the accounting system is referred to as double-entry accounting.
- You can automatically generate and send invoices using this accounting software.
Additionally, the balance sheet may be prepared according to GAAP or IFRS standards based on the region in which the company is located. These are some simple examples, but even the most complicated transactions can be recorded in a similar way. Because you make purchases with debt or capital, both sides of the equation must equal. This number is the sum of total earnings that were not paid to shareholders as dividends. Assets include cash and cash equivalents or liquid assets, which may include Treasury bills and certificates of deposit. This is the total amount of net income the company decides to keep.
Why Is the Accounting Equation Important?
For example, a positive change in plant, property, and equipment is equal to capital expenditure minus depreciation expense. If depreciation expense is known, capital expenditure can be calculated and included as a cash outflow under cash flow from investing in the cash flow statement. This account includes the total amount of long-term debt (excluding the current portion, if that account is present under current liabilities).

This line item includes all of the company’s intangible fixed assets, which may or may not be identifiable. Identifiable intangible assets include patents, licenses, and secret formulas. While the balance sheet and P&L statement have distinct purposes, they work together to provide a complete picture of a company’s financial well-being. Essentially, the balance sheet and P&L statement are partners in the financial world. We all know that we record all the business transactions using the Dual Aspect concept.
Components of a Balance Sheet
A company’s balance sheet is comprised of assets, liabilities, and equity. Assets represent things of value that a company owns and has in its possession, or something that will be received and can be measured objectively. Liabilities are what a company owes to others—creditors, suppliers, tax authorities, employees, etc. They are obligations that must be paid under certain conditions and time frames. Shareholder Equity is equal to a business’s total assets minus its total liabilities.
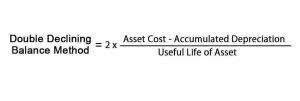
- Often, a company may depreciate capital assets in 5–7 years, meaning that the assets will show on the books as less than their “real” value, or what they would be worth on the secondary market.
- It breaks down net income and the transactions related to the owners (dividends, etc.).
- Our PRO users get lifetime access to our accounting equation visual tutorial, cheat sheet, flashcards, quick test, and more.
- Liabilities are claims on the company assets by other firms or people.
- This practice is referred to as “averaging,” and involves taking the year-end (2019 and 2020) figures—let’s say for total assets—and adding them together, and dividing the total by two.
- This is because creditors – parties that lend money such as banks – have the first claim to a company’s assets.
After you’ve identified your reporting date and period, you’ll need to tally your assets as of that date. It’s not uncommon for a balance sheet to take a few weeks to prepare after the reporting period has ended. Unearned revenue from the money you have yet to receive for services or products that you have not yet delivered is considered a liability. Rearrangement in such a way can be useful when looking at bankruptcy. The equation layout can help shareholders to see more easily how they will be compensated.
Guide to Understanding Accounts Receivable Days (A/R Days)
Public companies, on the other hand, are required to obtain external audits by public accountants, and must also ensure that their books are kept to a much higher standard. Balance sheets allow the user to get an at-a-glance view of the assets and liabilities what is the accounting equation of the company. In this example, Apple’s total assets of $323.8 billion is segregated towards the top of the report. This asset section is broken into current assets and non-current assets, and each of these categories is broken into more specific accounts.